New courses available now
Check out our first five courses:
https://argyll-business-school.teachable.com/
Now on the Teachable platform:
- An Introduction to Business
- Management and Leadership
- Your Introduction to Digital Marketing
- Start Your Own Health, Hair, Beauty Business
- How to Be a Better Student
Email us now for a special introductory offer of 20% off: argyllbusinessschool@gmail.com
(We also create bespoke business and business-related courses from £50).

Is it an X social media platform?
In recent years, X (formerly known as Twitter) has undergone significant transformations under Elon Musk’s leadership, prompting numerous UK brands to reevaluate their presence on the platform. This article delves into the compelling reasons why UK brands should consider departing from X, supported by recent developments and expert analyses.
1. Escalation of Misinformation and Hate Speech
Since Musk’s acquisition in 2022, X has faced criticism for its handling of misinformation and hate speech. The platform’s relaxed content moderation policies have led to a surge in disinformation, particularly during critical events like the 2023 Israel-Hamas conflict. Studies have shown that verified users, often referred to as “superspreaders,” were responsible for a significant portion of viral misinformation during this period.
The proliferation of harmful content not only tarnishes the platform’s reputation but also poses risks for brands associated with it. Advertising alongside such content can inadvertently link brands to controversial or offensive material, potentially alienating customers and damaging brand equity.
2. Decline in User Engagement
User engagement on X has experienced a notable decline. Reports indicate that daily active users decreased by 16% among mobile app users as of September 2023. Additionally, the UK’s Office of Communications (Ofcom) reported a drop in UK adults visiting the platform, from 26.5 million in 2022 to 22.2 million in 2023.
This downward trend suggests a diminishing audience reach for brands, reducing the effectiveness of marketing efforts on the platform. As users migrate to alternative platforms, brands may find greater engagement and return on investment elsewhere.
3. Advertiser Exodus and Brand Safety Concerns
The environment on X has prompted several high-profile advertisers to withdraw. A survey by Kantar revealed that 26% of advertisers plan to reduce their spending on X in 2025, citing concerns over brand safety due to the platform’s content moderation policies.
The departure of major advertisers underscores the challenges brands face in maintaining a safe and suitable environment for their messages. Continuing to advertise on X may expose brands to reputational risks associated with undesirable content.
4. High-Profile Departures Influencing Public Perception
Notable organizations and public figures have publicly exited X, influencing public perception. The Guardian, a leading UK news outlet with 10.7 million followers, ceased posting on X due to the prevalence of disturbing content, including racism and far-right conspiracy theories. Similarly, celebrities like Jamie Lee Curtis and Don Lemon deactivated their accounts following Musk’s political alignments.
These high-profile departures can sway public opinion, leading consumers to question the values of brands that remain on the platform. Aligning with platforms perceived negatively by the public can adversely affect brand reputation and customer loyalty.
5. Emergence of Alternative Platforms
The shifting social media landscape has introduced alternative platforms gaining traction among users and brands. Meta’s Threads reached over 275 million monthly users by November 2024, while Bluesky expanded to nearly 9 million users in the same period.
These platforms offer brands new avenues to engage with audiences in environments that may better align with their values and marketing objectives. Exploring these alternatives can provide opportunities for more effective and meaningful interactions with target demographics.
Conclusion
The evolving dynamics of X present significant considerations for UK brands evaluating their social media strategies. The rise in misinformation and hate speech, declining user engagement, advertiser withdrawals, high-profile exits, and the availability of alternative platforms collectively suggest that maintaining a presence on X may no longer serve the best interests of brands. By reassessing their digital engagement strategies and exploring other platforms, UK brands can better safeguard their reputation, ensure brand safety, and foster more positive connections with their audiences.

Business Plan No More
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the traditional business plan is increasingly viewed as outdated. Historically, these comprehensive documents, often spanning 30 to 50 pages, served as detailed roadmaps outlining a company’s objectives, strategies, and financial projections. However, the dynamic nature of modern markets has exposed several limitations of this conventional approach.
Limitations of Traditional Business Plans
1. Inflexibility: Traditional business plans can be rigid, making it challenging for companies to adapt to unforeseen changes or pivot when necessary. This rigidity may hinder responsiveness to market dynamics.
2. Time-Consuming Development: Crafting a detailed business plan demands significant time and resources, which could be better utilized in product development, market research, or customer engagement.
3. Rapid Obsolescence: In fast-paced industries, the assumptions and projections within a traditional business plan can quickly become outdated, rendering the document less useful for guiding strategic decisions.
Emergence of Agile Planning Alternatives
To address these challenges, many entrepreneurs and business leaders are adopting more agile and iterative planning methodologies that emphasize flexibility and real-time responsiveness. Notable alternatives include:
• Lean Startup Methodology: This approach advocates for rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative product development, enabling businesses to adapt swiftly based on customer feedback and market conditions.
• Business Model Canvas: A visual framework that allows companies to succinctly map out their value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances, facilitating quick adjustments as needed.
• Agile Business Plans: These focus on short-term objectives and immediate actions, allowing businesses to remain adaptable and responsive to changes, rather than adhering to a fixed long-term plan.
Advantages of Agile Planning
Adopting these flexible planning approaches offers several benefits:
• Enhanced Adaptability: Businesses can respond promptly to market shifts, technological advancements, and customer preferences, maintaining relevance and competitiveness.
• Resource Efficiency: By concentrating on immediate goals and iterative development, companies can allocate resources more effectively, reducing waste associated with extensive upfront planning.
• Improved Stakeholder Engagement: Concise and dynamic planning tools facilitate better communication with investors, employees, and customers, fostering alignment and collaboration.
Conclusion
While traditional business plans have played a significant role in business development, the contemporary market environment demands more agile and responsive planning methods. By embracing alternatives such as the Lean Startup Methodology, Business Model Canvas, and Agile Business Plans, companies can navigate uncertainty more effectively and position themselves for sustained success.

References
1. The Evolution of Business Plans – SMBCEO
• Discusses how business plans have evolved and why traditional plans may no longer be effective in today’s fast-paced environment.
2. Lean Canvas – Digital Enterprise
• Explores the Lean Canvas, a concise, one-page business model framework emphasizing agility and rapid iteration.
3. Customer Development – Wikipedia
• Introduces the Business Model Canvas and how it promotes testing, iteration, and customer-centric planning.
• Describes the IpOp Model, a strategic tool for pre-project analysis and opportunity evaluation.
5. Steve Blank on Lean Startup Methodology – Business Insider
• Highlights the importance of Lean Startup principles and why static business plans are being replaced by more dynamic frameworks.
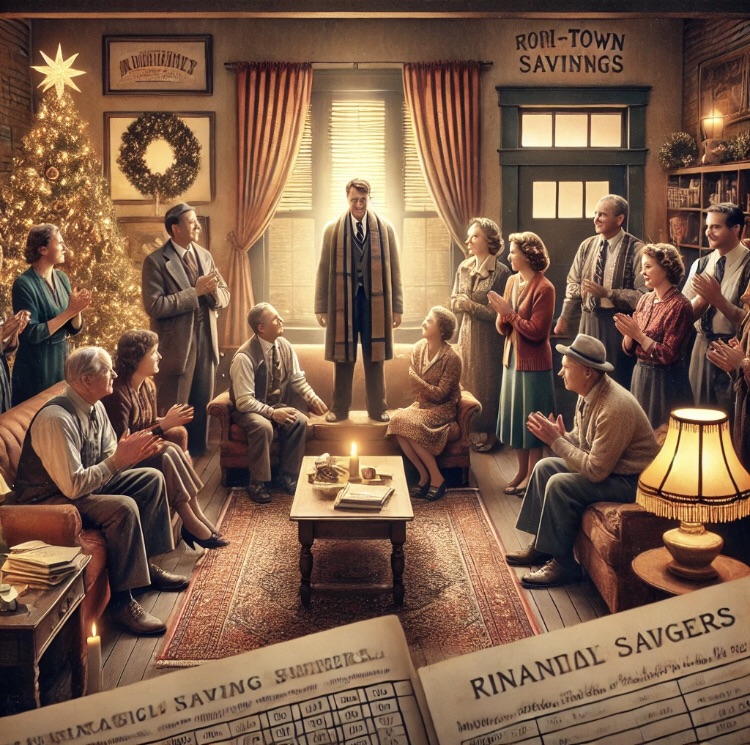
It’s a Wonderful Business Life
Frank Capra’s 1946 classic, It’s a Wonderful Life, offers enduring lessons for business leaders, emphasizing integrity, community, and the profound impact of individual actions.
1. Prioritize Integrity and Ethical Leadership
George Bailey’s unwavering commitment to ethical principles, even when faced with personal and professional challenges, underscores the importance of integrity in leadership. His refusal to compromise his values for financial gain fosters trust and loyalty within his community. Modern business leaders can draw from George’s example by maintaining transparency and ethical standards, which are foundational to sustainable success.
2. Value Community and Relationships
The film illustrates that a business’s true wealth lies in its relationships. George’s dedication to the residents of Bedford Falls, prioritizing their well-being over profit, cultivates a supportive community that ultimately rallies to his aid. This narrative highlights the significance of building strong, genuine connections with clients, employees, and stakeholders, reinforcing the idea that businesses thrive when they invest in their communities.
3. Embrace Adaptability and Resilience
Throughout the story, George confronts numerous unforeseen challenges, from financial crises to personal sacrifices. His resilience and ability to adapt to changing circumstances demonstrate the necessity for businesses to remain flexible and responsive in the face of adversity. Embracing change and maintaining a positive outlook can lead to innovative solutions and long-term success.
4. Recognize the Ripple Effect of Individual Actions
George’s realization of how his actions have positively impacted countless lives serves as a reminder that individual contributions can have far-reaching effects. Business leaders should acknowledge the potential of their decisions to influence not only their organizations but also the broader community and industry. By fostering a culture of responsibility and purpose, leaders can inspire their teams to contribute meaningfully.
5. Understand the Importance of Succession Planning
The challenges faced by the Bailey Building and Loan following the death of George’s father highlight the need for effective succession planning in business. Ensuring that leadership transitions are smooth and that successors are prepared to uphold the company’s values and mission is crucial for organizational continuity and stability.
In conclusion, It’s a Wonderful Life offers timeless insights into ethical leadership, the value of community, adaptability, the impact of individual actions, and the necessity of succession planning. By integrating these lessons, business leaders can navigate challenges with integrity and foster environments where both organizations and communities flourish

The GLOBAL Technique
One effective acronym to teach business concepts to international students could be “GLOBAL”—a memorable, business-relevant term that also relates to the international context.
G.L.O.B.A.L.: Core Aspects of Business Education
1. G — Goals and Strategy:
• Emphasize the importance of setting clear business goals and developing strategic plans. This includes the marketing plan.
• Help students understand different business objectives (profit, growth, market share) and strategies for achieving them.
2. L — Leadership and Management:
• Cover essential leadership skills, including communication, motivation, and ethical decision-making.
• Distinguish between management and leadership and teach how both roles are crucial to business success.
3. O — Operations and Logistics:
• Explain the basics of business operations, including supply chain management, production processes, and logistics.
• Introduce Lean and Six Sigma methodologies and discuss their relevance in international business.
4. B — Business Culture and Communication:
• Explore how different cultures impact business practices, communication styles, and negotiation.
• Teach intercultural communication skills to help students navigate and respect global business diversity.
5. A — Accounting and Finance:
• Cover fundamental financial literacy topics, including budgeting, financial reporting, and profitability analysis.
• Make sure students grasp key accounting principles and financial metrics used in assessing business health.
6. L — Legal and Ethical Standards:
• Familiarize students with international business laws, intellectual property rights, contracts, and compliance.
• Emphasize the role of ethics in business decisions, corporate responsibility, and sustainability.
Why “GLOBAL” Works
The GLOBAL acronym provides a structured yet flexible framework for introducing students to essential business concepts with an international focus. It’s easy to remember, culturally relevant, and well-suited for students from diverse backgrounds learning to navigate the business world. This approach also encourages students to see business as inherently global and interconnected, aligning with the needs of an international classroom.

Why Traditional Exams Aren’t Worthwhile for Business Students
Title: Why Traditional Exams Aren’t Worthwhile for Business Students
Exams have been a staple in education systems worldwide for centuries, seen as a crucial way to measure student knowledge and competence. However, in the realm of business education, it’s time to rethink this approach. Traditional exams may not be the most effective way to evaluate business students, nor do they align with the skills and real-world experience these students need to succeed in today’s dynamic marketplace. Here’s why exams for business students might not be worthwhile and what alternatives could better prepare them for the challenges ahead.

1. Lack of Real-World Application
The business world is fast-paced, complex, and constantly evolving. It requires skills that go beyond memorization and theoretical knowledge. Traditional exams often focus on a student’s ability to recall facts or solve hypothetical problems under timed conditions. While this might test short-term retention, it fails to mimic the actual challenges business professionals face daily, such as strategic decision-making, collaborative problem-solving, and negotiation.
Real-world business scenarios rarely come with a clear question or a multiple-choice answer. Business students benefit more from hands-on experiences, such as internships, project-based assessments, and case studies, which allow them to apply their knowledge in realistic and dynamic environments.
2. Stifles Critical Thinking and Creativity
Business success is built on innovation and adaptability. Traditional exams, however, can stifle critical thinking by encouraging students to memorize information rather than analyze, synthesize, and create new solutions. Business students need to develop these skills to navigate complex markets, identify opportunities, and develop innovative strategies.
Encouraging students to think outside the box, collaborate with others, and approach problems creatively is critical for business education. Alternative assessments such as presentations, group projects, and simulations can foster these skills better than traditional exams ever could.
3. Inconsistent with Modern Business Practices
Today’s business environment values continuous learning, adaptability, and the ability to work collaboratively in teams. Traditional exams don’t align with these values; instead, they promote individual performance and often place students in competition with one another rather than teaching them how to collaborate.
Business education should emphasize teamwork, leadership, and communication skills—attributes that are vital in the workplace. Group projects, collaborative assignments, and real-world consulting projects offer students the chance to work together, reflect on their learning, and receive feedback, simulating the collaborative nature of modern business practices.
4. One-Size-Fits-All Doesn’t Work for Business
Business students come from diverse backgrounds, each bringing unique skills and perspectives to the table. Traditional exams often use a one-size-fits-all approach that doesn’t account for these differences, potentially discouraging students who may excel in practical, creative, or interpersonal domains rather than in standardized testing environments.
By using diverse assessment methods, educators can cater to various learning styles, skills, and talents. For instance, a student might be a brilliant communicator and negotiator but struggle in an exam setting. Alternatives like role-playing exercises, business simulations, and real-life consulting projects allow students to leverage their strengths and demonstrate their competence in a way that reflects how they will contribute in the business world.
5. Exams Promote Short-Term Learning
Traditional exams often lead students to cram information to pass tests, only to forget much of it afterward. This approach prioritizes short-term gains over long-term, practical knowledge retention. Business students, however, need deep, applicable knowledge that they can draw upon as they face real-world challenges in their careers.
Active learning methods such as interactive workshops, case studies, and peer-led discussions help reinforce concepts more effectively than rote memorization. By encouraging students to engage with the material and apply it to practical situations, these methods foster long-term understanding and retention of business principles.
6. Fails to Measure Soft Skills
Success in business isn’t just about knowing the right answer—it’s also about emotional intelligence, communication, leadership, and negotiation skills. Traditional exams, with their focus on written responses and right-or-wrong outcomes, don’t effectively measure these soft skills, which are critical for success in business careers.
Instead of exams, evaluations could focus on presentations, group collaborations, or simulated business environments, where students must demonstrate these essential interpersonal skills. By shifting the focus from academic performance to practical ability, educators can better prepare students for the realities of working in a business setting.
The Way Forward: Alternative Assessment Methods
So, if traditional exams aren’t the answer, what is? Business schools should consider alternative methods that align more closely with the professional world. Here are a few suggestions:
• Project-Based Learning: Engaging students in long-term projects that mirror real-world business challenges allows them to apply theoretical knowledge and develop practical skills simultaneously.
• Case Studies: Analyzing and presenting solutions to case studies helps students think critically, work collaboratively, and apply their learning in a realistic context.
• Simulations and Role-Playing Exercises: These assessments allow students to immerse themselves in realistic scenarios, honing skills like leadership, negotiation, and decision-making under pressure.
• Internships and Experiential Learning: Integrating internships or experiential learning components into the curriculum provides students with hands-on experience, bridging the gap between academic concepts and their application in real business environments.
Conclusion
While traditional exams have their place in certain disciplines, they are increasingly out of touch with the skills business students need to thrive in a complex, rapidly evolving world. Business education should en masse move toward assessment methods that develop practical skills, foster critical thinking, and emphasize collaboration and creativity. By doing so, we can ensure that business students are better prepared not just to succeed academically, but to excel in their careers.
The Summer Disconnect: Why Business Teachers and Lecturers Switch Off During the Holidays
As the academic year draws to a close, the anticipation of a well-deserved break fills the air. For business teachers and lecturers, the summer holidays provide a critical opportunity to step away from the constant demands of teaching, grading, and administrative tasks. But why is it so essential for these educators to switch off during the summer, and what benefits does this downtime offer?
The Need for a Break
Teaching business courses is not just about delivering lectures; it’s an intensive job that requires significant preparation, ongoing professional development, and staying up-to-date with industry trends. The role is intellectually demanding and emotionally taxing. The summer break allows educators to recharge their batteries, ensuring they return to their classrooms refreshed and ready to inspire their students.
Benefits of Switching Off
1. Mental Health and Well-being The constant grind of the academic year can lead to burnout. Taking a complete break during the summer helps business educators to relax and rejuvenate. This time off is crucial for maintaining mental health, reducing stress levels, and preventing burnout. Engaging in leisure activities, spending time with family, or even indulging in a hobby can provide a much-needed mental health boost.
2. Professional Growth While it may seem counterintuitive, stepping away from work can actually enhance professional growth. The break provides educators with the space to reflect on the past academic year, assess their teaching methods, and identify areas for improvement. It also allows them to pursue personal development opportunities that are not directly related to their current curriculum, such as reading widely, traveling, or attending unrelated workshops. These experiences can provide fresh perspectives and ideas that can be brought back into the classroom.
3. Reconnecting with Passion Teaching is a passion-driven profession. The routine of the academic year can sometimes dull this passion, turning it into a mechanical job. Summer breaks give educators the chance to reconnect with why they chose this profession in the first place. Whether it’s through travel, reading, or simply taking time to reflect, these activities can reignite their enthusiasm and commitment to teaching.
4. Updating Industry Knowledge Business is a fast-paced field that is constantly evolving. Summer breaks give educators the time to catch up on the latest industry trends and developments. They can read new research papers, attend industry conferences, or engage with professionals in the field. This ensures that they bring the latest knowledge and insights into their classrooms, providing their students with a current and relevant education.
Strategies for Effective Disconnection
For many business teachers and lecturers, fully disconnecting from work can be challenging. Here are some strategies to ensure they make the most of their summer break:
• Set Boundaries: Clearly define the start and end of the holiday period. Communicate these boundaries to colleagues and students to minimize work-related interruptions.
• Digital Detox: Limit the use of emails and other work-related digital communications. Consider setting up an out-of-office message to manage expectations.
• Engage in Different Activities: Engage in activities that are completely unrelated to work. This could be anything from hiking to painting, which helps shift the focus away from professional responsibilities.
• Reflect and Plan: Use part of the break to reflect on the past year and make a loose plan for the upcoming academic year. This can provide a sense of control and reduce anxiety about returning to work.
Conclusion
The summer holidays are not just a luxury for business teachers and lecturers—they are a necessity. By fully switching off, these educators can recharge, reflect, and return to their classrooms with renewed energy and enthusiasm. This not only benefits their well-being but also enhances the quality of education they provide. So, as the summer sun shines brightly, let’s encourage our business educators to take that well-earned break and come back stronger than ever.

The Transformative Role of AI in Education
The AI revolution is happening. Fast.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the education sector, reshaping how students learn and educators teach. From personalized learning experiences to administrative efficiencies, AI’s impact on education is both profound and far-reaching.
Personalized Learning
One of the most significant contributions of AI in education is personalized learning. AI-driven platforms like Duolingo and Coursera use algorithms to adapt educational content to the individual needs of students. These platforms assess a learner’s strengths and weaknesses, providing customized exercises that enhance understanding and retention. This personalized approach not only increases engagement but also boosts academic performance by allowing students to learn at their own pace.
Intelligent Tutoring Systems
AI-powered intelligent tutoring systems, such as Carnegie Learning and Third Space Learning, provide students with on-demand assistance that mimics human tutoring. These systems use natural language processing to understand student queries and offer real-time feedback and support. By analyzing a student’s progress, AI tutors can adjust their teaching methods, ensuring that students receive the help they need when they need it most.
Automating Administrative Tasks
AI is also streamlining administrative processes, allowing educators to focus more on teaching and less on paperwork. Tools like Knewton and Gradescope automate tasks such as grading and attendance tracking, reducing the time teachers spend on these routine activities. By handling these mundane tasks, AI frees up educators to dedicate more time to lesson planning and one-on-one student interactions, enhancing the overall educational experience.
Enhancing Accessibility
AI is making education more accessible for students with disabilities. Text-to-speech and speech-to-text technologies, powered by AI, assist students with visual and hearing impairments. For example, apps like Voiceitt and Seeing AI help students with speech and vision impairments navigate their educational environments more effectively, ensuring that all students have equal opportunities to succeed.
Preparing for the Future
AI’s integration into education is not without challenges. Concerns about data privacy and the digital divide highlight the need for careful implementation and equitable access to technology. However, the benefits of AI in education cannot be overlooked. As AI continues to evolve, it will play a crucial role in preparing students for the future workforce, where digital literacy and adaptability are key.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AI is transforming education by personalizing learning, supporting educators, enhancing accessibility, and preparing students for a digital future. As educational institutions continue to embrace AI technologies, the potential for a more personalized, efficient, and inclusive learning environment becomes increasingly attainable. The future of education is bright, and AI is leading the way.
This post was written by AI

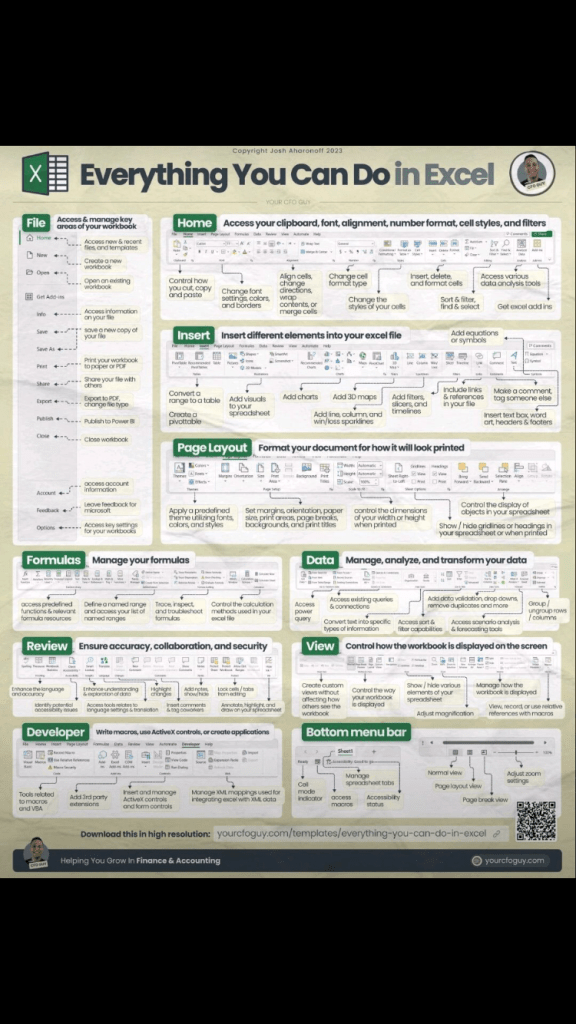
Excel hints